

![]()
Possibly useful information:
v =x /
t
a =
v /
t
v = vi + a t
x = xi+ v i t + (1/2) a t2
v = r
F = ma
F12 = - F21
w = m g
g = 9.8 m/s2 => 10 m/s2
(that is, use the approximation that g = 10 m/s 2 )
p = m v
Impulse = F
t =
p
Ptot,i = Ptot,f
W = F d
P =
W /
t
W =
KE
KE = (1/2) m v2
PEg = m g h
PEel = (1/2) k x 2
F = &endash; k x or Fext = k x
I =
m r 2
I(hoop) = M R 2; I(disk) = (1/2) M R 2
rot force = (moment arm) (force)
rot force = (rot mass) (ang accel)
ac = v 2 / r
Fg = G M m / r 2
T 2 / R 3 = constant
For every question, also consider as a possible answerE) none of the above
1. The four fundamental forces in the Universe are
A) atomic, friction, centripetal, gravityB) atomic, nuclear, friction, centripetal
C) gravity, friction, weight, atomic
D) gravity, electromagnetism, strong nuclear, and weak nuclear
2. Which of the following has the largest momentum relative to Earth?
A) a tightrope walker underneath a circus tentB) a sports car speeding along Route 16.
C) a cement truck sitting at a construction site.
D) the Science building on campus.
3. A moving object on which no forces are acting will continue to move with constant
A) non-zero accelerationB) impulse
C) momentum
Impulse = (force) x (time) = change in momentumTherefore, if the force is zero the change in momentum
must also be zero (or the momentum must be constant)
Or, you can go back to F = ma.
If the force is zero the acceleration is zero and that
means the velocity is constant and that, in turn,
means the momentum is constant.
D) all of these
4. Impulse, F ![]() t,
is equal to
t,
is equal to
A) kinetic energyB) momentum
C) change in momentum
D) change in kinetic energy
5. Conservation of momentum is directly related to
A) Newton's First Law of MotionB) Newton's Second Law of Motion
C) Newton's Third Law of Motion
F12 = - F21F12
t = - F21
t
p1 = -
p2
p1 +
p2 = 0
( p1 + p2 ) = 0
( p1 + p2 ) = constant
D) International shortages of momentum :-)
6. Two objects, A and B, have the same size and shape, but A is twice as heavy as B. When they are dropped simultaneously from a tower, they reach the ground at the same time, but A has a greater
A) momentumIf they reach the ground at the same time, we know they have the same speed (or velocity) so the one with the greater mass or weight must also have more momentum. They fall with the same accelerationB) acceleration
C) speed
D) all of the above
7. A car traveling along the highway needs a certain amount of force exerted on it to stop. More stopping force may be required when the car has
A) more massB) more momentum
C) less stopping distance
D) all of the above
8. A 6 kg ball has a momentum of 12 kg m/s. What is the ball's speed?
A) 2 m/smomentum = mass x velocity12 kg-m/s = (4 kg) x (2 m/s)
B) 3 m/s
C) 6 m/s
D) 72 m/s
9. A ball is moving at 4 m/s and has a momentum of 72 kg m/s. What is the ball's mass?
A) 9 kgB) 18 kg
momentum = mass x velocity72 kg-m/s = (18 kg) x (4 m/s)
C) 36 kg
D) 288 kg
10. Consider pushing two objects:
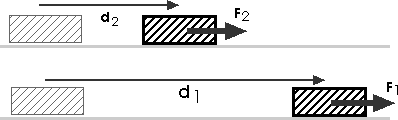
If you push object one twice as far as object two while applying the same force you do
A) half as much work as you do to object twoB) the same amount of work as you do to object two
C) twice as much work as you do to object two
W = F sW = F s
D) four times as much work as you do to object two
11. Consider pushing two objects:
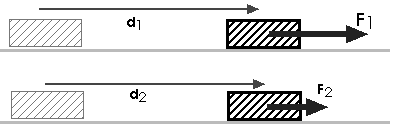
If you push the two objects the same distance but apply twice the force to object one, you do
A) half as much work as you do to object twoB) the same amount of work as you do to object two
C) twice as much work as you do to object two
W = F sW = F s
D) four times as much work as you do to object two
12. Exert 2 N for a distance of 2 m in 2 s and you deliver a power of
A) 0.5 WB) 1.0 W
C) 2.0 W
Power is the rate at which work is doneP =
W /
t
P = [(2 N) ( 2 m)] / (2 s)
P = 4 J / 2 s
P = 2 W
D) 4.0 W
13. Exert 200 J in 50 s and your power output is
A) 0.5 WB) 1.0 W
C) 2.0 W
D) 4.0 W
Power is the rate at which work is doneP =
W /
t
P = 200 J / 50 s
P = 4 W
14. An object is raised above the ground gaining a certain amount of potential energy. If the same object is raised twice as high it gains
A) half as much energyB) the same amount of energy
C) twice as much energy
PE = m g hD) four times as much energy
15. An object that has kinetic energy must be
A) elevated (an elevated object would have additional PEbut an elevated object can readily be at RESTand have no KE at all).
B) falling (an object moving UP also has KE)
C) moving
KE = (1/2) m v2D) at rest
16. An object that has potential energy may have this energy because of its
A) speedB) acceleration
C) momentum
D) position
17. Levers are an example of
A) simple machinesB) conservation of momentum
C) conservation of angular momentum
D) applications of Newton's Second Law, F = ma
18. When a car is braked to a stop, its kinetic energy is transformed to
A) energy of motionB) heat energy
C) stopping energy
D) potential energy
19. For which position does the ball on the end of the string have the greatest gravitational potential energy?
D) PE = m g hThe height is greatest at position D.
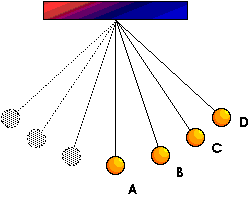
20. For which position above does the ball on the end of the string have the greatest kinetic energy?
A) KE = (1/2) m v2ETot = PE + KEKE = maximum when PE = minimum
PE = minimum at A
Therefore, KE = maximum at A
21. Which requires more work: lifting a 10 kg sack vertically 2 meters or lifting a 5 sack vertically 4 meters?
A) lifting the 5 kg sackB) both require the same amount of work
W = (force) x (distance)W = (mg) x (h)
W10kg = (10 kg) (10 m/s2) ( 2 m) = 200 J
W5kg = (5 kg) (10 m/s2) ( 4 m) = 200 J
C) lifting the 10 kg sack
D) both require the same amount of force
22. A 10 kg sack is lifted 2 meters in the same time as a 5 kg sack is lifted 4 meters. The power expended in raising the 10 kg sack compared to the power used to lift the 5 kg sack is
A) half as muchB) the same
W = (force) x (distance)W = (mg) x (h)
W10kg = (10 kg) (10 m/s2) ( 2 m) = 200 J
W5kg = (5 kg) (10 m/s2) ( 4 m) = 200 J
We have already seen, in the previous question,
that the work is the same.
Power =
W/
t
Since the times are the same, the power used in the two cases is also the SAME for the two cases.
C) twice as much
D) four times as much
23. A 5 kg mass is held 4 m above the ground. What is the approximate potential energy of the mass with respect to the ground?
A) 5 JB)50 J
C) 100 J
D) 200 J
PE = m g hPE = (5 kg) (10 m/s2) (4 m)
PE = 200 J
24. A 20 kg mass has 400 J of potential energy with respect to the ground. Approximately how far is it located above the ground?
A) 1 mB) 2 m
PE = m g hPE = (20 kg) (10 m/s2) (2 m)
PE = 400 J
h = 2m
C) 3 m
D) 4 m
25. Using 1,200 J of work, a model elevator is raised from the ground floor to the second floor in 20 seconds. How much power does the elevator use?
A) 60 WP = W / tP = 1,200 J / 20 s
P = 60 J / s
P = 60 W
B) 600 W
C) 2.4 kW
D) 24 kW
26. A car moves 4 times as fast as another identical car. Compared to the slower car, the faster car has
A) the same kinetic energyB) 4 times the kinetic energy
C) 8 times the kinetic energy
D) 16 times the kinetic energy
KE = (1/2) m v2If v is 4 times greater then v2 is 42 = 16 times greater.
27. A car moving at 30 km/hr skids 20 m with locked brakes. How far will the car skid with locked brakes if it is traveling at 90 km/hr?
A) 40 mB) 60 m
C) 90 m
D) 180 m
W = F s =KE
Increasing the speed by a factor of three means KE has increased by a factor of nine.
The brakes only exert so much force as they skid; the force is constant.
The stopping distance must increase by a factor of nine.
This was also a homework problem, Pb 6.1 .
28. When a rifle is fired it recoils so both the bullet and rifle are set in motion. The rifle and bullet ideally acquire equal but opposite amounts of
A) kinetic energyB) momentum
Momentum is always conservedC) potential energy
D) all of the above
29. What does an object have when moving that it doesn`t have when at rest?
A) momentumAt rest, an object's momentum must be zero.But an object can have potential energy while it is at rest.
And an object certainly has mass while it is at rest.
B) energy
C) mass
D) all of the above
30. If an object has kinetic energy, then it also must have
A) momentumB) velocity
C) speed
D) all of the above
If it has KE, it has velocity and that means it also has momentum and speed.
31. According to Kepler's laws, the paths of planets about the Sun are
A) spiralsB) parabolas
C) ellipses
D) hyperbolas
32. According to Newton, the greater the masses of interacting objects, the
A) greater the force of gravity, by the product of the massesF = G M m / d2B) less the force of gravity, inversely as the cube of the masses
C) greater the force of gravity, by the square of the masses
D) less the force of gravity, inversely as the square of the masses
33. According to Newton, the greater the distance between masses of interacting objects, the
A) greater the force of gravity, proportional to the distanceB) less the force of gravity, inversely as the distance
C) greater the force of gravity, proportional to the square of the distance
D) less the force of gravity, inversely as the square of the distance
F = G M m / d2
34. What is the force of gravity on a 500-newton woman standing on the earth's surface?
A) 9.8 NB) 50 N
C) 500 N
D) 5,000 N
35. If the mass of Earth somehow decreased with no change in radius, your weight would
A) increaseB) decrease
F = G M m / d2Making M smaller means the force (your weight) is also smaller.
C) stay the same
36. If the radius of Earth somehow increased with no change in mass, your weight would
A) increaseB) decrease
F = G M m / d2Making d larger means the force (your weight) is smaller.
C) stay the same
37. If Earth's radius increased to twice its original radius with no change in mass, then your weight would
A) decrease to one-quarter its original valueF = G M m / d2Increasing d to one-half its value means F, the force of gravity or your weight, will decrease to one-fourth its original value.
B) decrease to one-half its original value
C) remain the same
D) increase to twice its original value
38. The force of gravity acting on the Space Shuttle in orbit is nearly
A) zeroB) equal to the weight of the Space Shuttle at Earth's surface
F = G M m / d2In a low-Earth orbit, the Space Shuttle's distance from the center of Earth is nearly the same as it was at Earth's surface.
C) about one-tenth its weight at Earth's surface
D) about one-one hundredth its weight at Earth's surface
39. A woman who normally weighs 400 N stands on top of a very tall ladder so she is one earth radius above the earth's surface. How much would she weigh there?
A) zeroB) 100 N
F = G M m / d2If d is made twice as large, then d2 will be four times as large. Since we are dividing by d2, this means the Force -- her weight -- will be only one-fourth as much.
C) 200 N
D) 400 N
40. The force of gravity acts on all apples on an apple tree. Some apples are twice as far from the ground as others. These twice- as-high apples, for the same mass, have practically
A) one-fourth the weightB) one-half the weight
C) the same weight
F = G M m / d2Being twice as far above the ground has hardly any effect on d, the distance from the center of Earth to the apple.
D) twice the weight
41. The planet Jupiter is about 300 times as massive as Earth, yet on its surface you would weigh only about 3 times as much. This is because
A) your mass is 100 times less on Jupiter.B) Jupiter is significantly farther from the sun.
C) Jupiter's radius is 10 times Earth's radius.
D) you are 100 times more weightless there.
42. Horses that move with the fastest linear speed on a merry-go-round are located
A) nearer to the centerB) nearer to the edge
C) always white
D) in front of the slower ones
43. An industrial flywheel has a greater rotational inertia when most of its mass is
A) nearer the axisB) nearer the rim
C) spread out evenly
44. A [solid] cylinder and a ring roll down an incline starting at the same time. The one to reach the bottom first will be the
A) cylinderThe rotational mass of the ring -- with all its mass at the edge -- is I = M R2.The rotational mass of the solid disk or cylinder -- with its mass distributed throughout the cylinder or disk -- is I = (1/2) M R2.
That is, the cylinder has a smaller rotational mass. That means it -- the cylinder -- will win; it will roll down the inclined plane faster and reach the bottom first.
B) ring
C) neither; they both reach the bottom at the same time
45. Put a pipe over the end of a wrench when trying to turn a stubborn nut on a bolt, to effectively make the wrench handle twice as long, you'll increase the torque by
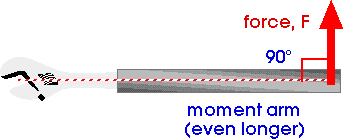
A) twotorque = rotational force = force x lever armIf we make the lever arm twice as great, we increase the torque by two.
B) four
C) eight
D) sixteen
46. When a twirling ice skater (or dizzy Physics professor) brings her (or his) arms inward, her (or his) rotational speed
A) increases
angular momentum = constantangular momentum = angular momentum
(rotational mass) x (rotational speed) =
= (rotational mass) x (rotational speed)
B) decreasesC) remains the same (or is conserved)
47. To pry open the top of a can of pain, it is best to use a screwdriver that has a handle that is
A) long and thinIt doesn't really need to be thin, but it does need to be long.B) thick or wide
C) short and stubby
D) slippery
48. A car travels in a circle with constant speed. The net force on the car is
A) directed forward, in the direction of travel.B) directed towards the center of the curve.
This is called the centripetal forceC) zero because the car is not accelerating.
Because the car changes its direction,it changes its velocity
and that means that it is accelerating!
D) directed backward, because of friction.
49. Newton's Law of Universal Gravitation was accepted because
A) Newton had a great and admirable reputation.B) Newton had been right earlier with his Laws of Motion.
C) its predictions were confirmed by Kepler's Laws of Planetary Motion and the observations upon which they were based.
This is the "hallmark" of modern Science.D) Galileo strongly endorsed the idea and encouraged Sir Isaac Newton.
Galileo died the year Newton was born.
50. When an ice skater wants to spin more rapidly, she
A) pulls her arms in close to her body to decrease her moment of inertia.angular momentum = angular momentum
(moment of inertia) x (rotational speed) =
= (moment of inertia) x (rotational speed)
B) extends her arms and leg to increase her moment of inertia.C) inhales deeply and holds her breath to increase her moment of inertia.
D) exhales deeply and holds her breath to avoid conservation of angular momentum.
![]()
(C) 1998 Doug Davis, all rights reserved