
PHY 3050C
Excursions in
Physics
Second Hour Exam
March 2, 2000
![]()
![]()

PHY 3050C
Excursions in
Physics
Second Hour Exam
March 2, 2000
![]()
![]()
Statistics:
High: 96Mean: 80
Low: 54
Enter all your answers in the "scantron sheet" or the "bubble
sheet". Turn in only that sheet. Anything you write on this exam will
not be seen or used or considered or graded. Be sure your name is on
the "bubble sheet" you hand in. Be sure your name is bubbled-in. Be
sure your answers are recorded correctly.
For every question, also consider the following as a possible
answer:
e) none of the above
a) measured in units of joules.
b) potential or kinetic.
c) considered as the ability to do work.
d) all of the above.
2. In the context of this course, conservation of energy means
a) energy is scarce and must be used wisely.
b) the difference between PE and KE (ie, PE - KE) is a constant.
c) energy is important or fundamental or conservative.
d) the value of the total energy remains constant.
3. If an object is in stable equilibrium, a small movement will cause
its center of mass to move
a) beyond its base of support.
b) lower.
c) higher.
d) closer to its geometric center.
4. Whenever an object moves in a circle, even at constant speed,
there is
a) an acceleration tangent to (or along) its circular path.
b) a force tangent to (or along) its circular path.
c) an acceleration directed along the radius, toward the center of the circle.
d) a force due to friction.
5. Consider a solid disk and a hoop that have the same radius and the
same mass. The “moment of inertia” or the “rotational
mass” of the solid disk is
a) smaller than
b) the same as
c) larger than
that of the hoop.
6. When an ice skater pulls her arms and leg in close to her axis of
rotation, she spins faster. This is an example of the conservation
of
a) energy.
b) momentum.
c) angular momentum.
d) natural resources.
7. According to Kepler’s Laws of Planetary Motion, planets move
faster when they are
a) closer to the Sun.
b) less massive.
c) more massive.
d) farther from the Sun.
8. Kepler’s Laws of Planetary Motion were
a) based upon the Ptolemaic System in which the Sun, the moon, and the planets revolved around Earth.
b) based upon a system in which all the planets, including Earth, revolved around the Sun in perfect circles.
c) based upon a lifetime of careful observation or experimental data of planetary positions
d) in direct opposition to Newtons Laws of Motion.
9. The Space Shuttle is in a low-Earth orbit where the force of
gravity is only slightly different from that at Earth’s surface.
The period of such a low-Earth orbit is about
a) 9 minutes
b) 90 minutes
c) 24 hours
d) 9 days
10. An effective communications satellite may be in a
geosynchronous orbit with a period of 24 hours. Such an orbit
has a radius of about
a) 400 km
b) 4,000 km
c) 40,000 km
d) 400,000 km
11. Work involves
a) mass multiplied by acceleration
b) mass multiplied by distance
c) force multiplied by distance
d) force multiplied by time

12. If you push an object twice as far while applying the same force you do
a) half as much work.
b) the same amount of work.
c) twice as much work.
d) four times as much work.

13. If you push an object just as far while applying twice the force you do
a) half as much work.
b) the same amount of work.
c) twice as much work.
d) four times as much work.
14. Exert 4 N for a distance of 3 m in 2 s and you deliver a power
of
a) 2.0 W
b) 4.0 W
c) 6.0 WP = W / tW = F d = (4 N)(3 m) = 12 N m = 12 J
P = 12 J / 2 s
P = 6 W
d) 8.0 W
15. Exert 1,200 J of work in 60 s and your power output is
a) 5 W
b) 10 W
c) 20 WP = W / tP = 1200 J / 60 s
P = 20 W
d) 40 W
16. An object is raised above the ground gaining a certain amount of
potential energy. If the same object is raised three times as
high it gains
a) one-third as much energy
b) the same amount of energy
c) three times as much energyPE = m g hd) nine times as much energy
17. An object that has kinetic energy must be
a) elevated
b) falling
c) movingKE = (1/2) m v2d) at rest
18. An object that has potential energy may have this energy because
of its
a) speed
b) acceleration
c) momentum
d) position
19. When a car is braked to a stop, its kinetic energy is transformed
to
a) energy of motion
b) heat energy
c) stopping energy
d) potential energy
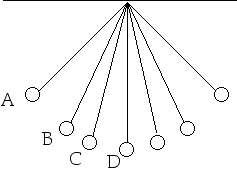
20. For which position above does the ball on the end of the string have the greatest gravitational potential energy?
a) greatest PEg
21. For which position above does the ball on the end of the string
have the greatest kinetic energy?
d) greatest KEKE is greatest where PE is leastand PE is least at position D
22. A 10 kg sack is lifted 4 meters in the same time as
a 5 kg sack is lifted 2 meters. The power expended in raising the 10
kg sack compared to the power used to lift the 5 kg sack is
a) one-fourth as much
b) one-half as much
c) the same
d) four times as muchP = W / tW = m g h
W1 = (10 kg)(10 m/s2)(4 m) = 400 J
W2 = (5 kg)(10 m/s2)(2 m) = 100 J
W1 = 4 W2
t1 = t2
P1 = 4 P2
23. A 3 kg mass is held 5 m above the ground. What is the approximate
potential energy of the mass with respect to the ground?
a) 15 J
b) 75 J
c) 150 JPE = m g hPE = (3 kg)(10 m/s2)(5 m)
PE = 150 J
d) 300 J
24. A 5 kg mass has 50 J of potential energy with respect to the
ground. Approximately how far is it located above the ground?
a) 0.5 m
b) 1 mPE = m g h50 J = (5 kg)(10 m/s2)( h )
h = 1 m
c) 5 m
d) 10 m
25. A car moves twice as fast as another identical car. Compared to
the slower car, the faster car has
a) the same kinetic energy
b) one-half the kinetic energy
c) twice the kinetic energy
d) four times the kinetic energyKE = (1/2) m v2That means that doubling the speed causes the KE to increase by a factor of four
since 22 = 4.
26. A car moving at 40 km/hr skids
20 m with locked brakes.
How far will the car skid with locked brakes if it is traveling at
120 km/hr?
a) 60 m
b) 90 m
c) 120 m
d) 180 mKE = (1/2) m v2That means that increasing the speed by a factor of three causes the KE to increase by a factor of nine since 32 = 9.
W = F d
Increasing the KE by a factor of 9 means the work done to bring the car to a stop also increases by a factor of 9. Once tires skid, the force of friction is essentially constant so that means the distance must also increase by a factor of nine.
27. When a rifle is fired it recoils so both the bullet and rifle are
set in motion. The rifle and bullet ideally acquire equal but
opposite amounts of
a) kinetic energy
b) momentum
c) potential energy
d) all of the above
28. What does an object have when moving that it doesn`t have
when at rest?
a) momentump = m vb) energy
An object can have PE and still be at rest.c) mass
An object always has mass.d) all of the above
29. If an object has kinetic energy, then it also must have
a) momentum
b) velocity
c) speed
d) all of the aboveKE = (1/2) m v2
30. According to Kepler's laws, the paths of planets about the Sun
are
a) straight lines
b) parabolas
c) ellipses
d) hyperbolas
31. According to Newton, the greater the masses of interacting
objects, the
a) greater the force of gravity, by the product of the massesFg = G M m / r2Fg = G M m / r2
b) less the force of gravity
c) greater the force of gravity, by the square of the masses
d) less the force of gravity, inversely as the square of the masses
32. According to Newton, the greater the distance between masses of
interacting objects, the
a) greater the force of gravity, proportional to the distance
b) less the force of gravity, inversely as the distance
c) greater the force of gravity, proportional to the square of the distance
d) less the force of gravity, inversely as the square of the distanceFg = G M m / r2Fg = G M m / r2
33. If the mass of Earth somehow
increased with no change in radius, your weight
would
a) increaseFg = G M m / r2Fg = G M m / r2
b) decrease
c) stay the same
34. If the radius of Earth somehow
decreased with no change in mass, your weight
would
a) increaseFg = G M m / r 2Fg = G M m / r 2
b) decrease
c) stay the same
35. If Earth's mass decreased to one-third its original mass
with no change in radius, then your weight would
a) decrease to one-ninth its original value
b) decrease to one-third its original valueFg = G M m / r2Fg = G M m / r2
c) increase to nine times its original value
d) increase to three times its original value
36. The force of gravity acting on the Space Shuttle in orbit is
nearly
a) zero
b) equal to the weight of the Space Shuttle at Earth's surfaceThis approximation may be called a "low-Earth orbit".c) about one-tenth its weight at Earth's surface
d) about one-one hundredth its weight at Earth's surface
37. A woman who normally weighs 500 N stands on top of a very tall
ladder so she is one Earth radius above the earth's surface. How much
would she weigh there?
a) zero
b) 125 NFg = G M m / r2If r is increased by a factor of two, the force of gravity is decreased by a factor of four since we are dividing by r2.
c) 250 N
d) 500 N
38. The force of gravity acts on all apples on an apple tree. Some
apples are twice as far from the ground as others. These twice-
as-high apples, for the same mass, have practically
a) one-fourth the weight
b) one-half the weight
c) the same weightFg = G M m / r2r is measured from the center of Earth and r is almost the same for apples at the top of the tree or for apples at the bottom of the tree.
d) twice the weight
39. The planet Jupiter is about 300 times as massive as Earth, yet on
its surface you would weigh only about 3 times as much. This is
because
a) your mass is 100 times less on Jupiter.
b) Jupiter is significantly farther from the sun.
c) Jupiter's radius is 10 times Earth's radius.This was homework question 8.15F = G M m / R2 MJ = 300 ME
FJ = 3 FE
FJ = G MJ m / RJ2 = 3 [ G ME m / RE2 ] = 3 FE
FJ = G (300 ME) m / RJ2 = 3 [ G ME m / RE2 ] = 3 FE
G (300 ME) m / RJ2 = 3 [ G ME m / RE2 ]
(300 ME) / RJ2 = 3 [ ME / RE2 ]
(300 ) / RJ2 = 3 [ 1 / RE2 ]
100 / RJ2 = 1 / RE2
RJ2 / 100 = RE2
RJ2 = 100 RE2
RJ = 10 RE
The radius of Jupiter is about ten times as large as the radius of Earth!d) you are 100 times more weightless there.
40. An industrial flywheel has a greater rotational inertia when most
of its mass is
a) nearer the axis
b) nearer the rim
c) spread out evenly
41. A hollow ring or hoop and a solid disk roll down an incline
starting at the same time. The one to reach the bottom first will be
the
a) hollow ringI = M r2b) solid disk
I = (1/2) M r2The solid disk has a smaller "rotational mass" (or "moment of inertia").
That means it is easier to accelerate.
Therefore it -- the solid disk -- will reach the bottom faster.
c) neither; they both reach the bottom at the same time
42. Put a pipe over the end of a wrench when trying to turn a
stubborn nut on a bolt, to effectively make the wrench handle
twice as long, you'll increase the torque by a factor
of
a) two
b) four
c) eight
d) sixteen
43. When a twirling ice skater extends her arms outward, her
rotational speed
a) increases
b) decreasesIt is the angular momentum that is conserved.Extending her arms increases her "rotational mass" I
I
= I
This means her rotational speed
will decrease.
c) remains the same (ie, her angular speed is conserved).
44. To turn a stubborn screw, it is best to use a screwdriver that
has a handle that is
a) long and thin
b) thick or wide
c) yellow
d) slippery
45. In Newton’s Law of Universal Gravitation, Fg = G M m/r2, the proportionality constant, “big G”, is very small; G = 6.67 x 10 - 11 N kg2/m2 . This means the force of gravity between two objects of common, ordinary, small masses is incredibly small. Nonetheless, Henry Cavendish devised a very sensitive way to measure these incredibly small forces. This allowed him to measure “big G”, the proportionality constant in Newton’s Law of Universal Gravitation. Once this constant was known, he could readily calculate
a) the radius of Earth.
b) the mass of Earth.Cavendish gave his talk or paper the title "Weighing the Earth".c) the radius of the moon’s orbit.
d) the mass of the moon.
46. A car travels in a circle with constant speed. The net force on
the car is
a) directed forward, in the direction of travel.
b) directed towards the center of the curve.This net force is called the centripetal force.c) zero because the car is not accelerating.
d) directed outward, away from the center of the curve
47. A communications satellite appears stationary to an Earth-based
observer. The orbit such a satellite is in is called a
a) low-Earth orbit.
b) polar orbit.
c) geosynchronous orbit.
d) high-Earth orbit.
48. As your kinetic energy is reduced to zero in an automobile crash,
use of seat belts means a stopping force is applied to your body over
a greater distance. This means the force on you is
a) less thanChange in KE = workwork = Force x distance
b) the same as
c) more than
if you were not wearing seat belts.
49. As you climb the first hill of a roller coaster, work is done by outside forces. At the top of that first hill, your velocity is nearly zero and you have maximum
a) momentum.
b) kinetic energy.
c) potential energy.PE = m g hd) weight.
50. A diver does a double saumersalt and then extends his body so
that his rotation nearly stops before going into the water. This is
an example of conservation of
a) momentum.
b) kinetic energy.
c) potential energy.
d) angular momentum.

(C) 2003, Doug Davis; all rights reserved