

Excursions in Physics
Third Hour Exam
March 31, 20023
Statistics:
High: 96
Mean: 76
Low: 46
![]()
![]()
For every question, also consider as a possible answer
E) none of the above
Be sure to fill in everything on the “scantron” sheet —
fill in the circles for your name and your social security number.
All I want is the “scantron” sheet; you may keep the exam questions.
![]()
![]()
For every question, also consider as a possible answer
E) none of the above
1. Increasing the mass of a simple pendulum harmonic oscillator makes its period
A) longer
B) shorter
C) unchanged
2. Increasing the mass m of a mass-and-spring simple harmonic oscillator makes
its period
A) longer
B) shorter
C) unchanged
3. A mass-and-spring simple harmonic oscillator has maximum kinetic energy
A) at its equilibrium position
B) when its displacement equals its amplitude
C) half way between equilibrium and amplitude
D) three-fourths of the way between equilibrium and amplitude
4. The period of a simple harmonic oscillator is
A) the time required for one oscillation
B) the number of oscillations per second
C) the energy stored in the oscillations
D) the maximum distance moved from equilibrium
5. The frequency of a certain oscillator is 100 Hz; its period is
A) 0.1 s
B) 0.01 s
C) 0.001 s
D) 0.0001 s
6. There are "signals" of many different frequencies coming into the
antenna of your radio. Only the one with a particular frequency is amplified
and produces the sound you listen to. This is an example of
A) resonance
B) damping
C) timbre or quality
D) fundamental regeneration
7. Which of the following is a longitudinal wave?
A) light
B) wave on a string
C) sound
D) all of the above
8. A wave has a frequency of 50 Hz and a wavelength of 0.5 m. It has a wave
speed of
A) 2.5 m/s
B) 10 m/s
C) 25 m/s
D) 100 m/s
9. A wave has a frequency of 32 Hz and travels 4 m in one second. It has
A) a wave speed of 128 m/s and a wavelength of 8 m.
B) a wave speed of 128 m/s and a wavelength of 1/8 m.
C) a wave speed of 4 m/s and a wavelength of 1/8 m
D) a wave speed of 4 m/s and a wavelength of 8 m
10. A wave has a frequency of 25 Hz and travels 5 m in one second. It has
A) a wave speed of 100 m/s and a wavelength of 5 m.
B) a wave speed of 100 m/s and a wavelength of 1/5 m.
C) a wave speed of 5 m/s and a wavelength of 1/5 m
D) a wave speed of 5 m/s and a wavelength of 5 m
11. For standing waves on a string,
A) a node is located at each end
B) a whole number times half the wavelength equals the length of the string
C) the whole "pattern" of standing waves occurs only for certain frequencies
D) all of the above
12. For standing waves on a string, the distance between adjacent nodes is always
A) the length of the string
B) one wavelength
C) one half the wavelength
D) half the length of the string
13. For standing waves on a string, the distance between adjacent antinodes
is always
A) half the length of the string
B) one half the wavelength
C) one wavelength
D) the length of the string
14. A bobber on a fishing line oscillates up and down two (2) times per second
as waves pass by. The waves have a wavelength of 25 cm. The waves are traveling
at
A) 12.5 cm/s
B) 25 cm/s
C) 50 cm/s
D) 100 cm/s
15. Sound is
A) an electromagnetic wave
B) a polarized wave
C) a longitudinal wave
D) all of the above
16. " Infrasonic" means
A) lower than the range of human hearing
B) higher than the range of human hearing
C) faster than the speed of sound
D) slower than the speed of sound
17. Bats and dolphins use echolocation to navigate or the find food or to find
their way without relying on sight. The frequencies they use are
A) supersonic
B) infrasonic
C) ultrasonic
D) microsonic
18. The range of human hearing is about
A) 10 Hz to 100 Hz
B) 50 Hz to 500 Hz
C) 50 Hz to 20 kHz
k means kilo as in kilohertz or kilogram
There are 1,000 grams in a kilogram.
There are 1,000 Hz in a kHz.
D) 1 kHz to 100 kHz
19. Ella Fitzgerald made commercials for Memorex in which she used her voice
to break a wine glass. This is an example of
A) echolocation
B) supersonic sound
C) ultrasonic frequencies
D) resonance
20. Beats are heard when two sounds have
A) nearly the same amplitude
B) nearly the same frequencies
C) twice the amplitude
D) exactly twice the frequency
21. The fundamental frequency present in a sound is the
A) sum of all the frequencies mixed together
B) difference between the highest and lowest frequencies present
C) lowest frequency present
D) highest frequency present
22. The fundamental frequency present in a sound determines the
A) quality or timbre
B) amplitude or loudness
C) pitch or note
D) all of the above
23. The "pitch" of a sound is determined by its
A) overtones frequencies
B) harmonics frequencies
C) fundamental frequency
D) resonance frequency
24. The quality or timbre -- the distincitive characteristic -- of a sound is
determined by its
A) overtones or harmonics
B) amplitude or loudness
C) attack or decay
D) fundamental frequency
25. Consider a musical note of 262 hertz (middle “C”). Two octaves
higher is represented by a musical note
of
A) 131 Hz; this is one ocatave lower.
B) 524 Hz; this is one ocatave higher.
C) 1048 Hz
D) 1572 Hz
26. Suppose you play a note of a certain pitch on a violin. You can produce
a higher-pitched note by
A) shortening the length of the string that is allowed
to vibrate
B) decreasing the tension of the string (loosening the string)
C) increasing the linear mass density of the string (using a "heavier"
string)
D) lengthening the part of the string that vibrates.
27. When a flute sound is viewed on an oscilloscope, the sound wave is very
smooth. This is because
A) the amplitude is always small (flutes are quiet)
B) it has practically no overtones or harmonics
C) its fundamental frequency has a smaller amplitude than its second and third
harmonics
D) its harmonics get larger and larger
28. When a trumpet sound is viewed on an oscilloscope, the sound wave is very
complex. This is because
A) the amplitude is always large (trumpets are loud)
B) it has practically no overtones or harmonics
C) it has many overtones or harmonics
D) its has only even-numbered overtones or harmonics
29. A petroleum geologist might use a very carefully calibrated simple pendulum
to do “prospecting” for a large pool of oil. If this “prospector”
were over such a large pool of oil, she or he would find the period of this
simple pendulum to be
A) longer
![]()
Directly above the large oil pool, the acceleration due to gravity, g, will be slightly less than normal.
this means the period T will be larger or longer than
normal.
B) shorter
C) unchanged
than normal.
30. Increasing the length of a simple pendulum makes its period
A) longer
![]()
B) shorter
C) unchanged
31. The period of a simple pendulum depends upon its
A) mass
B) amplitude
C) length
![]()
32. Ordinary household electricity is alternating current with a frequency of
60 Hz. Its period is
A) 60 cycles per second.
B) 120 cycles per second.
C) 0.0333 s.
D) 0.0167 s.
33. If you apply a force to an oscillator at its natural
frequency, you will produce motion
A) at exactly twice that frequency
B) at exactly one-half that frequency
C) with an amplitude that dies out or gets smaller.
D) with large amplitude
This is resonance.
34. As the amplitude of a simple harmonic oscillator increases, its frequency
A) increases
B) stays the same
C) decreases
35. Which of these waves can not be polarized?
A) light
B) sound
Sound is a longitudinal wave.
C) electromagnetic
D) wave on a string
36. Individual disturbance that make up a longitudinal
wave
A) move perpendicular to the direction of the wave
B) move parallel to the direction of the wave
C) move in circles
D) move in ellipses
37. On a string that is 1.0 m long, standing waves may be formed with the following
wavelengths:
A) 1.0 m, 2.0 m, 3.0 m
B) 1.0 m, 2.0 m, 4.0 m
C) 1.0 m, 0.67 m, 0.40 m
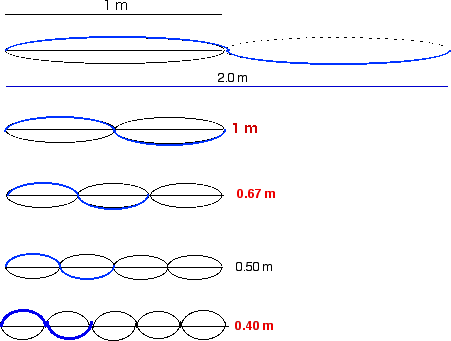
D) 1.0 m, 0.8 m, 0.75 m
38. Two waves can pass through each other; this is described by or as
A) an elastic collision
B) an inelastic collision
C) a supersonic collision
D) superposition
39. Suppose you strike two tuning forks and hear a beat frequency of 2 Hz.
You know that one of the tuning forks is tuned to 440 Hz. The other tuning fork
must have a frequency of
A) 2 x 440 Hz = 880 Hz.
B) 440 Hz / 2 = 220 Hz
C) (440 + 2) Hz = 442 Hz
Of course, (440 - 2)Hz = 438 Hz would also produce the
same beat frequency.
D) (440)2 = 193,600 Hz
40. If you double the frequency of a sound, you also double its
A) amplitude
B) wavelength; the wavelength is reduced to one-half
C) speed
D) all of the above
E) None of the above.
41. If you double the frequency of a sound, you reduce to one-half its
A) amplitude
B) wavelength
C) speed
D) all of the above
42. Sound travels fastest in
A) vacuum
B) air (gas)
C) water (liquid)
D) steek (solid)
43. “Supersonic” means
A) above the range of human hearing.
B) below the range of human hearing.
C) slower than the speed of sound.
D) faster than the speed of sound.
44. When or where two sound waves add together to produce a region of high
volume or large amplitude, we describe this as
A) destructive interference.
B) constructive interference.
C) reconstructive interference.
D) demonstrative interference.
45. Think of the sound produced when you blow across the top of a Coke bottle.
As you add water to the Coke bottle, so the column of air in the bottle becomes
shorter, you expect the pitch of the sound produced to
A) increase.
B) remain the same.
C) decrease.
46. Individual disturbance that make up a transverse wave
A) move perpendicular to the direction of the wave
B) move parallel to the direction of the wave
C) move in circles
D) move in ellipses
47. Simple harmonic motion is a common response for a disturbance from
A) unstable equilibrium.
B) constructive equilibrium.
C) stable equilibrium.
D) destructive equilibrium.
48. Damped harmonic motion means
A) harmonic motion connected with a fluid.
B) harmonic motion under water!
C) harmonic motion with a decreasing amplitude.
D) harmonic motion with an increasing frequency.
49. Amplitude is
A) frequency x period.
B) frequency / period.
C) maximum displacement from equilibrium.
D) maximum frequency.
50. Compared to ordinary sound, ultrasound has a
A) greater speed.
B) greater wavelength.
C) smaller wavelength.
D) slower speed.
![]()
![]()